RADIAL EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCKWAVE THERAPY (RESWT) has emerged as a transformative modality for treating musculoskeletal injuries. With a foundation in strong scientific evidence and FDA approvals, rESWT provides a noninvasive and effective solution for various conditions. Advanced devices, such as the enPulsPro, exemplify how technology continues to refine the application of this therapy, offering chiropractors precision and reliability without sacrificing accessibility.
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) originated in the 1980s as a breakthrough treatment for kidney stones, employing focused shockwaves (fESWT) to fragment stones without invasive surgery. Its potential in musculoskeletal medicine was discovered in the early 1990s when researchers observed its ability to promote bone healing and reduce calcifications in tendons.
Radial shockwave therapy, a variant introduced in the early 2000s, delivers acoustic waves in a radial, lowto medium-energy pattern, making it particularly suited for superficial soft tissue injuries. Over the past two decades, rESWT has gained widespread acceptance, with FDA approvals for chronic plantar fasciitis in 2002 and additional indications for tendinopathies and calcifications in subsequent years.
Radial shockwave therapy achieves therapeutic effects through biomechanical and biological mechanisms, which stimulate the body’s innate healing processes:
1. Neovascularization and Angiogenesis: Shockwaves induce microtrauma in treated tissues, prompting the release of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). This promotes new blood vessel formation, which is essential for oxygenating damaged tissues and accelerating healing.
2. Collagen Remodeling: Fibroblast activation leads to increased collagen synthesis and proper alignment, which is critical for repairing tendons and ligaments.
3. Pain Modulation: By reducing levels of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CORP), rESWT decreases pain perception. Additionally, it disrupts chronic pain pathways through neural desensitization.
4. Calcification Resorption: In conditions such as calcific shoulder tendinitis, rESWT helps fragment and resorb calcifications, restoring normal tendon structure.
These mechanisms are supported by clinical research, which underscores rESWT’s effectiveness for chronic conditions that often resist conventional treatments.
A robust body of evidence validates rESWT’s efficacy. A 2020 meta-analysis in Clinical Rehabilitation reviewed 25 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving over 1,800 patients with chronic tendinopathies, demonstrating significant improvements in pain and function compared to placebo or standard therapies.
A study published in Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery (2021) found that rESWT reduced pain by 60% in patients with chronic plantar fasciitis after three sessions and improved functionality by 77% at 12 weeks. These outcomes highlight rESWT’s ability to provide long-lasting relief for challenging musculoskeletal conditions.
By the third session, the patient reported a 50% reduction in pain, and by the fifth session, his VAS score dropped to 2/10.
In a 2021 study by Scholten et al. published in the European Journal of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine, radial shockwave devices, including the enPulsPro, were shown to be effective in reducing pain and improving mobility in patients with lateral epicondylitis. The study emphasized rESWT’s safety and versatility, making it a viable option for integrating into diverse clinical settings.
Radial extracorporeal shockwave therapy is particularly effective for conditions characterized by chronic inflammation, fibrosis, or calcification. Common indications include:
• Plantar fasciitis
• Achilles tendinopathy
• Patellar tendinopathy
• Lateral/medial epicondylitis
• Rotator cuff tendinopathy
• Myofascial pain syndromes
Treatment protocols may vary based on individual patient needs, but they commonly follow these parameters:
• Frequency: Once weekly for three to six weeks.
• Energy Levels: 60 to 185 mJ, adjusted for comfort and tissue type.
• Pulses Per Session: 2,000 to 3,000 pulses per treatment site.
• Session Duration: Five to ten minutes.
Devices allow chiropractors to fine-tune these parameters, enhancing clinical outcomes by delivering energy precisely and consistently. For example, the enPulsPro’s adjustable frequency (8 to 15 Hz) and energy levels ensure the therapy can be customized for varying tissue depths and patient sensitivities without sacrificing efficacy.
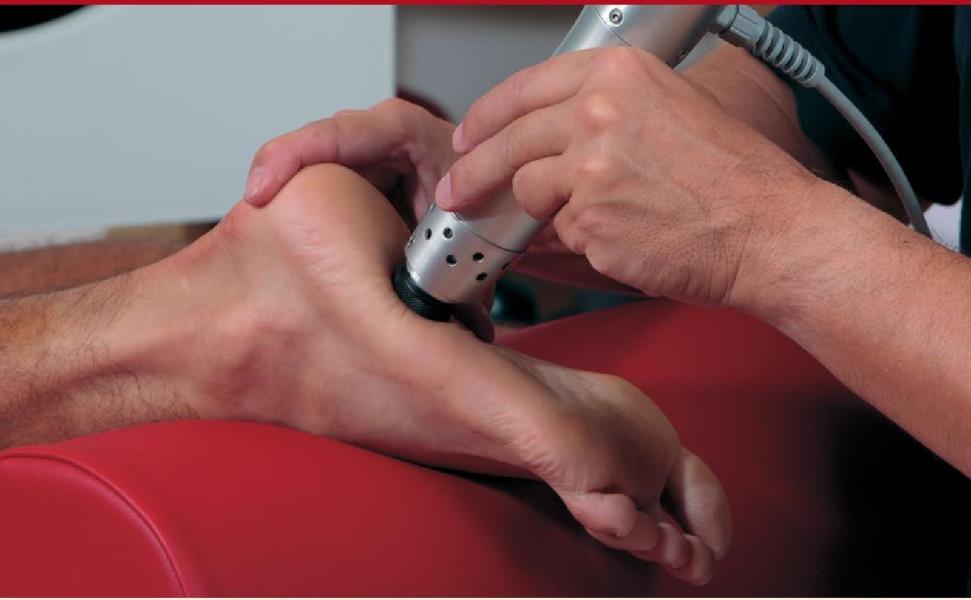
Patient Profile: A 48-year-old male presented with a six-month history of chronic plantarfasciitis. Despite attempting orthotics, stretching, and NSAIDs, his symptoms persisted, with pain rated at 7/10 on the visual analog scale (VAS) and limited functional mobility.
• Device: Radial shockwave therapy system.
• Energy Level: 90 mJ.
• Frequency: 12 Hz.
• Pulses Per Session: 2,500.
• Sessions: Weekly for five weeks.
• Outcome: By the third session, the patient reported a 50% reduction in pain, and by the fifth session, his VAS score dropped to 2/10. Functional improvements included the ability to walk 5,000 steps per day without discomfort. At the three-month follow-up, the patient maintained these improvements, demonstrating the long-term benefits of rESWT.
This case minors findings in the literature and highlights the value of evidence-based protocols.
Radial shockwave therapy has received FDA approval for several conditions, including chronic plantar fasciitis and calcific shoulder tendinitis. The therapy is well-tolerated with minor, transient side effects, such as redness, swelling, or mild soreness at the treatment site. Contraindications inelude active infections, malignancies, coagulopathies, and pregnancy.
The safety and reliability of devices further enhance the therapy’s appeal. Studies have shown that these systems deliver consistent energy levels while minimizing patient discomfort, making them a trusted choice in chiropractic and physical medicine.
For chiropractors, adopting rESWT offers an opportunity to expand treatment options while adhering to evidence-based care. To maximize success:
1. Training: Proper training ensures optimal use of the technology and improved patient outcomes.
2. Patient Education: Clearly explain the therapy’s science, expected outcomes, and minimal risks to foster trust ad compliance.
3. Outcome Measurement: Use validated tools like the VAS and the Foot and Ankle Ability Measure (FAAM) to track patient progress and document results.
Radial extracorporeal shockwave therapy represents a pivotal advancement in conservative musculoskeletal care. Backed by decades of research and enhanced by modern technology, such as the enPulsPro system, rESWT is redefining recovery for patients with chronic pain and injuries. By integrating this modality, chiropractors can offer cutting-edge, patient-centered care that aligns with the profession’s commitment to innovation and evidence-based practice.

Davis McAlister, DC, MEd, MS, BS, BA, CSCS, is an author, speaker, veteran, and sports chiropractor with more than 20 years of experience. He coaches strength and conditioning and powerlifting and works with high-performance athletes. He has served as a sideline physician for the WNBA, XFL, PRCA, and more. He holds degrees from Mississippi State, Sul Ross State, and Parker University, including a Doctor of Chiropractic. Dr. McAlister is also a key speaker for Zimmer MedizinSystems. Learn more about this technology at www.ZimmerUSA.com or by calling 800-327-3576.
References
1. Gollwitzer, H., et al. (2021). “Radial extracorporeal shockwave therapy for chronic plantar fasciitis: A randomized, controlled trial.” Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery, 141(7), 1021-1030.
2. Grady J, Boumendjel Y, LaViolette K, Smolinski T. Extracorporeal pulse-activated therapy versus injection: treatment of recalcitrant plantar fasciitis. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2019 Mar; 109(2): 108-112. doi: 10.7547/17-075. PMID: 31135197.
3. Mani-Babu, S., et al. (2020). “The effectiveness of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in common lower limb conditions: A systematic review including quantification of patient-rated pain reduction.” Clinical Rehabilitation, 34(2), 259-272.
4. Notarnicola, A., et al. (2022). “Efficacy of radial shockwave therapy for the treatment of lateral epicondylitis: A randomized controlled trial.” Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research, 17(1), 72.
5. Scholten P. Effectiveness of enPulsPro radial shockwave therapy for musculoskeletal conditions: A retrospective analysis. European Journal of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine. 2021; 57(6): 789-797.
 View Full Issue
View Full Issue






